Samacheer Kalvi textbook 12th Accountancy Accounts from Incomplete Records Text Book Back Questions and Answers
You can Download Accountancy Chapter 1 Accounts from Incomplete Records Questions and Answers, Reduced syllabus Guide Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi textbook 12th Accountancy Book answers Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Reduced Syllabus and score more marks in your public Examination.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi Textbook 12th Accountancy Question and answer Chapter 1 Accounts from Incomplete Records
Samacheer Kalvi textbook 12th Accountancy Accounts from Incomplete Records Text Book Back Questions and Answers
12th Accountancy Lesson 1 Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
Incomplete records are generally maintained by …………….
(a) A company
(b) Government
(c) Small sized sole trader business
(d) Multinational enterprises
Answer:
(c) Small sized sole trader business
Question 2.
Statement of affairs is a …………….
(a) Statement of income and expenditure
(b) Statement of assets and liabilities
(c) Summary of cash transactions
(d) Summary of credit transactions
Answer:
(b) Statement of assets and liabilities
Question 3.
Opening statement of affairs is usually prepared to find out the …………….
(a) Capital in the beginning of the year
(b) Capital at the end of the year
(c) Profit made during the year
(d) Loss occurred during the year
Answer:
(a) Capital in the beginning of the year
Question 4.
The excess of assets over liabilities is …………….
(a) Loss
(b) Cash
(c) Capital
(d) Profit
Answer:
(c) Capital
Question 5.
Which of the following items relating to bills payable is transferred to total creditors account?
(a) Opening balance of bills payable
(b) Closing balance of bills payable
(c) Bills payable accepted during the year
(d) Cash paid for bills payable
Answer:
(c) Bills payable accepted during the year
Question 6.
The amount of credit sales can be computed from …………….
(a) Total debtors account
(b) Total creditors account
(c) Bills receivable account
(d) Bills payable account
Answer:
(a) Total debtors account
Question 7.
Which one of the following statements is not true in relation to incomplete records?
(a) It is an unscientific method of recording transactions
(b) Records are maintained only for cash and personal accounts
(c) It is suitable for all types of organisations
(d) Tax authorities do not accept
Answer:
(c) It is suitable for all types of organisations
Question 8.
What is the amount of capital of the proprietor, if his assets are ₹ 85,000 and liabilities are ₹ 21,000?
(a) ₹ 85,000
(b) ₹ 1,06,000
(c) ₹ 21,000
(d) ₹ 64,000
Answer:
(d) ₹ 64,000
Question 9.
When capital in the beginning is ₹ 10,000, drawings during the year is ₹ 6,000, profit made during the year is ₹ 2,000 and the additional capital introduced is ₹ 3,000, find out the amount of capital at the end …………….
(a) ₹ 9,000
(b) ₹ 11,000
(c) ₹ 21,000
(d) ₹ 3,000
Answer:
(a) ₹ 9,000
Question 10.
Opening balance of debtors: ₹ 30,000, cash received: ₹ 1,00,000, credit sales: ₹ 90,000; closing balance of debtors is …………….
(a) ₹ 30,000
(b) ₹ 1,30,000
(c) ₹ 40,000
(d) ₹ 20,000
Answer:
(d) ₹ 20,000
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by incomplete records?
Answer:
- When accounting records are not strictly maintained according to double entry system, these records are called incomplete accounting records.
- Generally, cash accounts and the personal accounts of customers and creditors are maintained fully and other accounts are maintained based on necessity.
Question 2.
State the accounts generally maintained by small sized sole trader when double entry accounting system is not followed.
Answer:
- Generally cash account and the personal accounts of customers and creditors are maintained by small sized sole trader. When double entry accounting system is not followed.
Question 3.
What is a statement of affairs?
Answer:
- A statement of affairs is a statement showing the balances of assets and liabilities on a particular date. The balance of assets are shown on the right side and the balance of liabilities on the left side. This statement resembles a balance sheet. The difference between the total of assets and total of liabilities is taken as captial.
Capital = Assets – Liabilities.
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the features of incomplete records?
Answer:
Nature:
- It is an unscientific and unsystematic way of recording transactions.
- Accounting principles and accounting standards are not followed properly.
- 2. Types of accounts maintained – In general only cash and personal accounts are maintained fully. Real accounts and nominal accounts are not maintained properly. Some transactions are correctly omitted.
- 3. Lack of uniformity – There is no uniformity in recording the transactions among different organisations. Different organisations record their transactions according to their needs and conveniences.
- 4. Financial statements may not represent true and fair view – Due to the incomplete information and inaccurate records of accounts, the profit or loss calculated from these records cannot be relied upon. It may not represent true profitability. Assets and liabilities may not represent a true and fair view of financial position.
- 5. Suitability – Only the business concerns which have no legal obligation to maintain books of accounts under double entry system may maintain incomplete records. Hence, it may be maintained by small sized sole traders and partnership firms.
- 6. Mixing up of personal and business transactions – Generally, personal transactions of the owners are mixed up the with the business transactions. For example, purchase of goods for own use may be mixed up along with business purchases.
Question 2.
What are the limitations of incomplete records?
Answer:
- Limitations of Incomplete records:
- 1. Lack of proper maintenance of records – It is an unscientific and unsystematic way of maintaining records. Real and nominal accounts are not maintained properly.
- 2. Difficulty in preparing trial balance – As accounts are not maintained for all items, the accounting records are incomplete. Hence, it is difficult to prepare trail balance to check the arithmetical accuracy of accounts.
- 3. Difficulty in ascertaining true profitability of the business – Profit is found out based on available information and estimates. Hence, it is difficult to prepare ascertain true profit as the trading and profit and loss account cannot be prepared with accuracy.
- 4. Difficulty in ascertaining financial position – In general, only the estimated values of assets and liabilities are available from incomplete records. Hence, it is difficult to ascertain true and fair view of state of affairs or financial position as on a particular date
- 5. Errors and frauds cannot be detected easily – As only partial records are available, it may not be possible to have internal checks in maintaining accounts to detect errors and frauds.
- 6. Unacceptable to government and other activities – As accounts maintained are incomplete, these may not comply with the legal requirements. Hence, government, tax authorities and other legal authorities do not accept accounts prepared from incomplete records.
Question 3.
State the differences between double entry system and incomplete records.
Answer:
Question 4.
State the procedure for calculating profit or loss through statement of affairs.
Answer:
- The difference between the closing capital and the opening capital is taken as profit or loss of the business. Due adjustments are to be made for any withdrawal of capital from the business and for the additional capital introduced in the business.
Adjusting closing capital = Closing capital + Drawings – Opening capital.
Closing capital + Drawings – Additional capital – Opening capital = Proft/Loss.
Question 5.
Differentiate between statement of affairs and balance sheet.
Answer:
Question 6.
How is the amount of credit sale ascertained from incomplete records?
Answer:
Ascertainment of Credit Sales:-
IV. Exercises:1 to 20
Question 1.
From the following particulars ascertain profit or loss:
Answer:
Statement of profit or Loss
Question 2.
From the following particulars ascertain profit or loss:
Answer:
Statement of profit or Loss
Question 3.
From the following details, calculate the missing figure:
Answer:
Statement of profit or Loss
Question 4.
From the following details, calculate the capital as on 31st December 2018.
Answer:Statement of profit or Loss
Question 5.
From the following details, calculate the missing figure:
Answer:
Statement of profit or Loss
Question 6.
Following are the balances in the books of Thomas as on 31st March 2019.
Prepare a statement of affairs as on 31st March 2019 and calculate capital as at that date.
Answer:
Statement of profit or Loss
Question 7.
On 1st April 2018 Subha started her business with a capital of ₹ 1,20,000. She did not maintain proper book of accounts. Following particulars are available from her books as on 31.3.2019.
During the year she withdrew ₹ 30,000 for her personal use. She introduced further capital of? 40,000 during the year. Calculate her profit or loss.
Answer:
Statement of Affairs
Statement of profit or Loss
Question 8.
Raju does not keep proper books of accounts. Following details are taken from his records.
During the year he introduced further capital of ₹ 50,000 and withdrew ₹ 2,500 per month from the business for his personal use. Prepare statement of profit or loss with the above information.
Answer:
Statement of Affairs
Statement of profit or Loss
Question 9.
Ananth does not keep his books under double entry system. Find the profit or loss made by him for the year ending 31st March, 2019.
Ananth had withdrawn ₹ 60,000 for his personal use. He had introduced ₹ 17,000 as capita for expansion of his business. Create a provision of 5% on debtors. Plant and machinery is to be depreciated at 10%.
Answer:
Statement of Affairs
Statement of profit or Loss
Question 10.
Find out credit sales from the following information:
Answer:
Total / Sundry debtors Account
Question 11.
From the following details find out total sales made during the year.
Total / Sundry debtors Account
Total Sales = Cash Sales + Credit Sales
= 4, 60, 000 + 5, 40, 000
= 10, 00, 000
Question 12.
From the following particulars, prepare bills receivable account and compute the bills received from the debtors.
Answer:
Total/Bills Receivable Account
Question 13.
From the following particulars, calculate total sales.
Answer:
Bills Receivable Account
Debtors A/c
Total Sales = Cash Sales + Credit Sales
= 9, 85, 000 + 3, 15, 000
= ₹ 10, 00, 000
Question 14.
From the following details, calculate credit purchases.
Answer:
Total/ Sundry Creditors Account
Question 15.
From the following particulars calculate total purchases.
Answer:
Bills Payable Account
Total Creditors Account
Total purchases = Cash purchases + Credit purchases
Total purchases = 1, 55, 000 + 2, 25, 000
= Rs. 3, 80, 000
Question 16.
From the following details you are required to calculate credit sales and credit purchases by preparing total debtors account, total creditors account, bills receivable account and bills payable account.
Answer:
Bills Receivable A/c
Total debtors A/c
Bills Payable A/c
Total Creditors A/c
Question 17.
From the following details of Abdul who maintains incomplete records, prepare Trading and Profit and Loss account for the year ended 31st March, 2018 and a Balance Sheet as on the date.
Other details:
Answer:
Total Debtors Account
Total Creditors Account
Trading Account for year ended 31st March 2019
Profit/Loss Account for the year ended 31st March 2019
Balance Sheet as on 31st March 2019
Question 18.
Bharathi does not maintain her books of accounts under double entry system. From the following details prepare trading and profit and loss account for the year ending 31st March, 2019 and a balance sheet as on that date.
Cash Book
Other information:
Answer:
Total Debtors Account
Trading Account for that year ended 31st March 2019
Profit/Loss Account for the year ended 31st March 2019
Balance Sheet as on 31st March 2019
Question 19.
Arjun carries on grocery business and does not keep his books on double entry basis. The following particulars have been extracted from his books:
Other information for the year ending 31 – 3 – 2019 showed the following:
Total sales during the year were ₹ 7, 70,000. Purchases returns during the year were ₹ 30, 000 and sales returns were ₹ 25, 000. Depreciate plant and machinery by 5%. Provide ₹ 1, 500 for doubtful debts. Prepare trading and profit and loss account for the year ending 31st March, 2019 and a balance sheet as on the date.
Answer:
Statement of Affairs
Total Credit Account
Trading Account for year ended 31st December 2019
Profit/Loss Account for the year ended 31st December 2019
Balance Sheet as on 31st December 2019
Question 20.
Selvam does not keep his books under double entry system. From the following information prepare trading and profit and loss account A/c and balance sheet as on 31 – 12 – 2018.
Adjustments:
Write off depreciation of 5% on furniture. Create a reserve of 1% on debtors for doubtful debts.
Answer:
Statement of affairs as on 1st January, 2018
Answer:
Statement of Affairs as on st January, 2018
Trading Account for year ended 31st December 2018
Profit/Loss Account for the year ended 31st December 2018
Balance Sheet as on 31st December 2018
12th Accountancy Solutions Accounts from Incomplete Records Additional Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Single entry system is …………….
(a) a scientific method
(b) an incomplete double entry system
(c) None of these
Answer:
(b) an incomplete double entry system
Question 2.
Single entry system will not be accepted by …………….
(a) Proprietor
(b) Partners
(c) Tax authorities
Answer:
(c) Tax authorities
Question 3.
Single entry system capital is calculated.
(a) Capital = Assets – Liabilities
(b) Assets = Capital – Liabilities
(c) Capital = Assets + Liabilities
(d) Assets = Liabilities – Capital
Answer:
(a) Capital = Assets – Liabilities
Question 4.
Credit Purchase is obtained from …………….
(a) Total Debtors Accounts
(b) Total Creditors Account
(c) Statement of Affairs
Answer:
(b) Total Creditors Account
Question 5.
Statement of Affairs is like a …………….
(a) Trading Account
(b) Profit and Loss Account
(c) Balance Sheet
Answer:
(c) Balance Sheet
II. Fill in the blanks
Question 6.
Statement of affairs method is also called ……………. method.
Answer:
Networth Method.
Question 7.
A statement of affairs resembles a …………….
Answer:
Balance Sheet.
Question 8.
Single entry system maintains ……………. and ……………. accounts.
Answer:
Cash, Personal.
Question 9.
A firm has assets worth ₹ 10,00,000 and Capital ₹ 2,25,000 then its liabilities is …………….
Answer:
₹ 7,75,000.
Question 10.
The difference between capital while beginning and capital at the end indicates ……………. of the business.
Answer:
Profit/Loss.
Question 11.
The excess of assets over liabilities is …………….
Answer:
Capital.
III. Match the following
Question 12.

Answer:
(i) 3
Question 13.

Answer:
(ii) 3
IV. Assertion & Reason
Question 14.
(A) Assertion: Bill receivable endorsed are debited to Creditors Account
(B) Reason: Bills receivable is received from Debtors is credited to Debtors A/c
(a) Both (A) and (B) are correct
(b) (A) is correct and (B) is in correct
(c) Both are correct
(d) (A) is incorrect but (B) is correct
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (B) are correct
V. True or False
Question 15.
Limited Companies are free to choose either single entry (or) Double entry system.
Answer:
False.
Question 16.
Under networth method profit is ascertained by calculating the increase in network after adjusting for drawing and addition to capital.
Answer:
True.
Question 17.
Net Profit is calculated to capital at the end + Drawing + Capital introduced – Capital in the beginning.
Answer:
False.
Question 18.
In this system personal accounts and cash accounts transaction are recorded.
Answer:
True.
VI. Very Short Answer Question
Question 1.
Define of Single Entry System.
Answer:
According to Kohler, “Single Entry System is a system of Book-keeping in which as a rule, only records of cash and personal accounts are maintained. It is always incomplete double entry system varying with circumstances.
VII. Exercise
Question 1.
Calculate the profit for the following information.

Answer:

Question 2.
Calculate opening capital

Answer:

Question 3.
Calculate the missing figure.

Answer:

Question 4.
Joseph maintains books in single entry. Following details are given from his books.
He has taken ₹ 40,000 from the business for his personal exp depreciate furniture by 10%. Prepare a statement showing profit or loss for the year 2001.
Answer:
Statement of Affairs on 1.1.2010 to 31.12.2010

Statement Profit

Question 5.
From the following details find out the credit purchases and total purchase.

Answer:
Bills Payable Account
Total Creditors Account
Credit Purchase ₹ 30,800
Total Purchases = Cr Purchases + Cash Purchases
= 30, 800 + 29, 000
= ₹ 59, 800
Question 6.
From the following information you are required to calculate total sales.
Answer:
Bills Receivable Account
Total Debtors Account
Total Sales = Cash Sales + Credit Sales
= 40, 900 + 95, 300
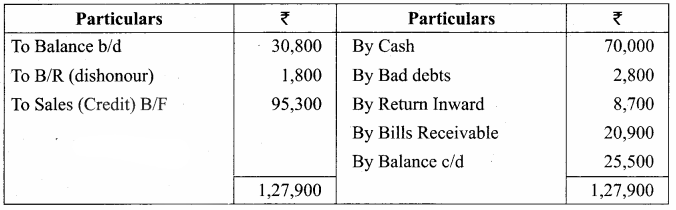
= ₹ 1,36,200
Question 7.
From the following particulars prepare the final accounts of Mrs. Meenakshi for the year ended 31.3.2004
Answer:
Total Debtors Account
Sundry Creditors Account
Question 8.
How to prepare the final accounts from incomplete records?
Answer:
- When books of accounts are incomplete, information regarding revenues, expenses, assets and liabilities is not known fully. Hence it becomes difficult to prepare trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet.
Steps to be followed to prepare final accounts:
- Opening statement of affairs is to be prepared to ascertain the opening capital.
- Missing figures must be found out with available date. This can be done by preparing memorandum accounts or by making necessary adjustments to the existing figure.
- It may become necessary to prepare a cash book find out missing items such as cash purchase and sales.
- By preparing total debtors and total creditors A/c credit sales and credit purchases can be ascertained.
- Bills Receivable, Bills Payable A/cs are to be prepared to find out the balance of Bills Receivable. Bills Payable accepted.
- The final step is to prepare trading and profit and loss A/c and balance sheet.
























































































0 Comments:
Post a Comment