Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Solutions Chapter 3 p-Block Elements – II - Tamilnadu state board
Tamilnadu state board 12th chemistry Guide solutions New reduced Syllabus book back Question and answer guide PDF download also available here. SamacheerGuide.online
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry p-Block Elements – II TextBook Evalution
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
In which of the following, NH₃ is not used?
(a) Nessler’s reagent
(b) Reagent for the analysis of IV group basic radical
(c) Reagent for the analysis of III group basic radical
(d) Tollen’s reagent
Answer:
(a) Nessler’s reagent
Question 2.
Which is time regarding nitrogen?
(a) least electronegative element
(b) has low ionisation enthalpy than oxygen
(c) d-orbitals available
(d) ability to form pπ – pπ bonds with itself
Answer:
(d) ability to form pπ – pπ bonds with itself
Question 3.
An element belongs to group 15 and 3 rd period of the periodic table, its electronic configuration would be …………
(a) 1s²2s²2p⁴
(b) 1s²2s²2p3
(c) 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p²
(d) 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p³
Answer:
(d) 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p³
Question 4.
Solid (A) reacts with strong aqueous NaOH liberating a foul smelling gas(B) which spontaneously bum in air giving smoky rings. A and B are respectively …………
(a) P₄(red) and PH₃
(b) P₄(white) and PH₃
(c) S₈ and H₂S
(d) P₄(white) and H₂S
Answer:
(b) P₄(white) and PH₃
Question 5.
In the brown ring test, brown colour of the ring is due to …………
(a) a mixture of NO and NO₂
(b) Nitroso ferrous sulphate
(c) Ferrous nitrate
(d) Ferric nitrate
Answer:
(b) Nitroso ferrous sulphate
Question 6.
On hydrolysis, PCl₃ gives …………
(a) H₃PO₃
(b) PH3
(c) H₃PO₄
(d) POOL
Answer:
(a) H₃PO₃
Question 7.
P₄O₆ reacts with cold water to give …………
(a) H₃PO₃
(b) H₄P₂O₇
(c) HPO₃
(d) H₃PO₄
Answer:
(a) H₃PO₃
Question 8.
The basicity of pyrophosphorous acid ( H₄P₂O₅) is …………
(a) 4
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 5
Answer:
(b) 2
Question 9.
The molarity of given orthophosphoric acid solution is 2M. its normality is …………
(a) 6N
(b) 4N
(c) 2N
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) 6N
Question 10.
Assertion – bond dissociation energy of fluorine is greater than chlorine gas
Reason – chlorine has more electronic repulsion than fluorine
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
(d) Both assertion and reason are false. The converse is true.
Question 11.
Among the following, which is the strongest oxidizing agent?
(a) Cl₂
(b) F₂
(c) Br₂
(d) I₂
Answer:
(b) F₂
Question 12.
The correct order of the thermal stability of hydrogen halide is …………
(a) HI > HBr > HCl > HF
(b) HF > HCl > HBr > HI
(c) HCl > HF > HBr > HI
(d) HI > HCl > HF > HBr
Answer:
(b) HF > HCl > HBr > HI
Question 13.
Which one of the following compounds is not formed?
(a) XeOF₄
(b) XeO₃
(c) XeF₂
(d) NeF₂
Answer:
(d) NeF₂
Question 14.
Most easily liquefiable gas is …………
(a) Ar
(b) Ne
(c) He
(d) Kr
Answer:
(c) He
Question 15.
XeF₆ on complete hydrolysis produces …………
(a) XeOF₄
(b) XeO₂F₄
(c) XeO₃
(d) XeO₂
Answer:
(c) XeO₃
Question 16.
On oxidation with iodine, sulphite ion is transformed to …………
(a) S₄` O _{ 6 }^{ 2- }`
(b) S₂` O _{ 2- }^{ 6 }`
(c) S` O _{ 2- }^{ 4 }`
(d) S` O _{ 2- }^{ 3 }`
Answer:
(c) SO`{ O } _ { 2- }^{ 4 }`
Question 17.
Which of the following is strongest acid among all?
(a) HI
(b) HF
(c) HBr
(d) HCl
Answer:
(a) HI
Question 18.
Which one of the following orders is correct for the bond dissociation enthalpy of halogen molecules?
(a) Br₂ > I₂ > F₂ > Cl₂
(b) F₂> Cl₂ > Br₂ > I₂
(c) I₂ > Br₂ > Cl₂ > F₂
(d) Cl₂> Br₂ > F₂ > I₂
Answer:
(d) Cl₂ > Br₂ > F₂ > I₂
Question 19.
Among the following the correct order of acidity is …………
(a) HClO₂ < HCIO < HClO₃ < HClO₄
(b) HClO₄ < HClO₂ < HCIO < HClO₃
(c) HClO₃ < HClO₄ < HClO₂ < HCIO
(d) HCIO < HClO₂ < HClO₃ < HClO₄
Answer:
(d) HCIO < HClO₂ < HClO₃ < HClO₄
Question 20.
When copper is heated with cone HNO₃ it produces …………
(a) CU(NO₃)₂ , NO and NO₂
(b) Cu(NO₃)₂ and N₂O
(c) CU(NO₃)₂ and NO₂
(d) Cu(NO₃)₂ and NO
Answer:
(c) CU(NO₃)₂ and NO₂
II. Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
What is inert pair effect?
Answer:
In p-block elements, as we go down the group, two electrons present in the valence s-orbital become inert and are not available for bonding (only p-orbital involves chemical bonding). This is called inert pair effect.
Question 2.
Chalcogens belongs to p-block. Give reason.
Answer:
- Chalcogens are ore forming elements. Most of the ores are oxides and sulphides, therefore oxygen, sulphur and other group 16 elements are called Chalcogens.
- In O, S, Se, Te and Po last electron enters to p-orbital. Therefore Chalcogens belongs to p-block.
Question 3.
Explain why fluorine always exhibit an oxidation state of -1?
Answer:
- Fluorine the most electronegative element than other halogens and cannot exhibit any positive oxidation state.
- Fluorine does not have d-orbital while other halogens have d-orbitals. Therefore fluorine always exhibit an oxidation state of-1 and others in halogen family shows +1, +3, +5 and +7 oxidation states.
Question 4.
Give the oxidation state of halogen in the following.
- OF₂
- O₂F₂
- Cl₂O₃
- I₂O₄
Answer:
1.OF₂
+2 + 2(x) = 0
+2 = -2x
2x = -2
x =-1
2. O₂F₂
2(+1) + 2x = 0
2x = – 2
x = – 1
3. Cl₂O₃
2(x) + 3(-2) =0
2x = +6
x = +3
4. I₂O₄
2(x) + 4(-2) =0
2x = +8
x = +4
Question 5.
What are interhalogen compounds? Give examples.
Answer:
- Each halogen combines with other halogens to form a series of compounds called interhalogen compounds. For example, Fluorine reacts readily with oxygen and forms difluorine oxide (F₂O) and difluorine dioxide (F₂O₂).
Question 6.
Why fluorine is more reactive than other halogens?
Answer:
- Fluorine is the most reactive element among halogen. This is due to the minimum value of F – F bond dissociation energy. Hence fluorine is more reactive than other halogens.
Give the uses of helium.
Answer:
- Helium and oxygen mixture is used by divers in place of air oxygen mixture. This prevents the painful dangerous condition called bends.
- Helium is used to provide inert atmosphere in electric arc welding of metals
- Helium has lowest boiling point hence used in cryogenics (low temperature science).
- It is much less denser than air and hence used for filling air balloons
Question 8.
What is the hybridisation of iodine in IF₇? Give its structure.
Answer:
- Hybridisation of iodine in IF₇ is sp³d³ Structure of IF₇ is pentagonal bipyramidal.
Question 9.
Give the balanced equation for the reaction between chlorine with cold NaOH and hot NaOH.
Answer:
1. Reaction between chlorine with cold NaOH:
Cl₂+ H₂O → HCl + HOCl
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂
Overall reaction
- Chlorine reacts with cold NaOH to give sodium chloride and sodium hypochlorite.
2. Reaction between chlorine with hot NaOH:
Cl₂ + H₂O → HCl + HOCl
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O
HOCl + NaOH → NaOCl + H₂O
3NaOCl → NaClO₃+ 2NaCl
Overall reaction
- Chlorine reacts with hot NaOH to give sodium chlorate and sodium chloride.
Question 10.
How will you prepare chlorine in the laboratory?
Answer:
1. Chlorine is prepared by the action of cone, sulphuric acid on chlorides in presence of manganese dioxide.
4NaCl + MnO₂+ 4H₂SO₄→ Cl₂ + MnCl₂ + 4NaHSO₄ + 2H₂O
2. It can also be prepared by oxidising hydrochloric acid using various oxidising agents such as manganese dioxide, lead dioxide, potassium permanganate or dichromate.
PbO₂ + 4HCl → PbCl₂ + 2H₂O + Cl₂
MnO₂ + 4HCl → MnCl₂ + 2H₂O + Cl₂
2KMnO₄+ 16HCl → 2KCl + 2MnCl + 8H₂O + 5Cl₂
K₂Cr₂O₇ + 14HCl → 2KCl + 2CrCl₃ + 7H₂O + 3Cl₂
3. When bleaching powder is treated with mineral acids chlorine is liberated
CaOCl₂ + 2HCl → CaCl₂ + H₂O + Cl₂
CaOCl₂ + H₂SO₄ → CaSO₄ + H₂O + Cl₂
Question 11.
Give the uses of sulphuric acid.
Answer:
- Sulphuric acid is used in the manufacture of fertilisers, ammonium sulphate and super phosphates and other chemicals such as hydrochloric acid, nitric acid etc.
- It is used as a drying agent and also used in the preparation of pigments, explosives etc.
Question 12.
Give a reason to support that sulphuric acid is a dehydrating agent.
Answer:
- Sulphuric acid is highly soluble in water and has strong affinity towards water and hence it can be used as a dehydrating agent. When dissolved in water it forms mono ( H₂SO₄. H₂O ) and di ( H₂SO₄. 2H₂O ) hydrates and the reaction is exothermic. The dehydration property can also be illustrated by its reaction with organic compounds such as sugar, oxalic acid and formic acid.
Question 13.
Write the reason for the anamolous behaviour of Nitrogen.
Answer:
1. Due to its small size, high electro negativity, high ionisation enthalpy and absence of d-orbitals.
2. N, has a unique ability to form pπ – pπ multiple bond whereas the heavier members of this group (15) do not form pπ – pπ bond, because their atomic orbitals are so large and diffused that they cannot have effective overlapping.
3. Nitrogen exists a diatomic molecule with triple bond between the two atoms whereas other elements form single bond in the elemental state.
4. N cannot form dπ – pπ bond due to the absence of d – orbitals whereas other elements can.
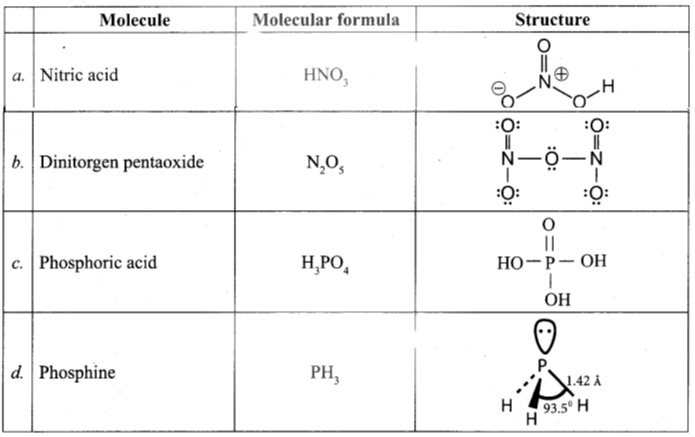
Question 14.
Write the molecular formula and structural formula for the following molecules.
(a) Nitric acid
(b) dinitrogen pentoxide
(c) phosphoric acid
(d) phosphine
Answer:
Question 15.
Give the uses of argon.
Answer:
- Argon prevents the oxidation of hot filament and prolongs the life in filament bulbs.
Question 16.
Write the valence shell electronic configuration of group-15 elements.
Answer:
General electronic configuration of group 15 elements are ns²np³
- Nitrogen – [He] 2s² 2p³
- Phosphorous – [Ne] 3s² 3p³
- Arsenic – [Ar] 3d¹⁰ 4s² 4p³
- Antimony – [Kr] 4d¹⁰ 5s² 5p³
- Bismuth – [Ne] 4f¹⁴ 5s¹⁰ 6s² 6p³
Question 17.
Give two equations to illustrate the chemical behaviour of phosphine.
Answer:
1. Phosphine reacts with halogens to give phosphorous penta halides.
PH₃ + 4Cl₂ → PCl₅ + 3HCl
2. Phosphine forms coordination compound with lewis acids such as boron trichloride.
3. Phosphine precipitates some metal from their salt solutions.
3AgNO₃ + PH₃→ Ag₃P + 3HNO₃
Question 18.
Give a reaction between nitric acid and a basic oxide.
Answer:
- Nitric acid reacts with bases and basic oxides to form salts and water.
ZnO + 2HNO₃ → Zn(NO₃)₂ + H₂O
3FeO + 10HNO₃ → 3Fe(NO₃)₃+ NO + 5H₂O
Question 19.
What happens when PCl₅ is heated?
Answer:
- On heating phosphorous pentachloride, it decomposes into phosphorus trichloride and chlorine.
PCl₅ `\underrightarrow { \triangle }`PCl₃ + Cl₂
Question 20.
Suggest a reason why HF is a weak acid, whereas binary acids of the all other halogens are strong acids.
Answer:
- The hydrogen halides are extremely soluble in water due to the ionisation.
X + H₂O → H₃O⁺ + X⁻
( X = F, Cl, Br or I )
- Solutions of hydrogen halides are therefore acidic and known as hydrohalic acids. Hydrochloric, hydrobromic and hydroiodic acids are almost completely ionised and are therefore strong acids but HF is a weak acid. For HF,
HF + H2o ⇌ H3o⁺ + F⁻
HF + F⁻ → HF–2
- At high concentration, the equilibrium involves the removal of fluoride ions is important. Since it affects the dissociation of hydrogen fluoride, therefore it is a weak acid.
Deduce the oxidation number of oxygen in hypofluorous acid – HOF.
Answer:
- In case of O – F bond is HOF, fluorine is most electronegative element. So its oxidation number is -1. Thereby oxidation number of O is +1. Similarly in case of O – H bond is HOF. O is highly electronegative than H.
- So its oxidation number is -1 and oxidation number of H is +1. So, Net oxidation of oxygen is – 1 + 1 = 0.
Question 22.
What type of hybridisation occur in
BrF₅
BrF₃
Answer:
1. BrF₅
BrF₅ is a AX₅type. Therefore is has sp³d² hybridisation. Hence, BrF₅ molecule has square pyramidal shape.
2. BrF₃
BrF₃ is a AX₃ type. Therefore it has sp³d hybridisation. Hence, BrF₃ molecule has T-shape.
Question 23.
Complete the following reactions.
Answer:
SamacheerGuide 12th Chemistry p-Block Elements – II Evaluate yourself
Question 1.
Write the products formed in the reaction of nitric acid (both dilute and concentrated) with zinc.
Answer:
Samacheer book 12th Chemistry p-Block Elements – II Additional Questions
Samacheer Book 12th Chemistry p-Block Elements – II 1 Mark Questions and Answers
I. Choose the best answer.
Question 1.
About 78% of earth atmosphere contains,…………
(a) P
(b) As
(c) N
(d) Bi
Answer:
(c) N
Question 2.
Which one of the following is not a pnictogens?
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Oxygen
(c) Phosphorous
(d) Antimony
Answer:
(b) Oxygen
Question 3.
Which one of the following shows isotopes?
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Arsenic
(c) Antimony
(d) Bismuth
Answer:
(a) Nitrogen
Question 4.
Nitrogen gas in atmosphere is separated industrially from liquid air by …………
(a) simple distillation
(b) Fractional distillation
(c) Sublimation
(d) Distillation under reduced pressure
Answer:
(b) Fractional distillation
Question 5.
Bond order for nitrogen molecule is …………
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 0
Answer:
(c) 3
Question 6.
Nitrogen gas is …………
(a) Inert
(b) Noble
(c) More reactive
(d) Less reactive
Answer:
(a) Inert
Question 7.
Which one of the following is used in cryosurgery?
(a) Liq N₂
(b) Liq NH₃
(c) Liq Na
(d) Liq H₂
Answer:
(a) Liq N₂
Question 8.
The dielectric constant of ammonia is (K) …………
(a) 10⁻³⁰
(b) 10⁻¹⁴
(c) 10³⁰
(d) 10¹⁴
Answer:
(a) 10⁻³⁹
Question 9.
When ammonia reacts with copper sulphate solution to give complex, the colour of complex is …………
(a) violet
(b) deep blue
(c) blue
(d) Red
Answer:
(b) deep blue
Question 10.
H – N – H bond angle in NH₃ is …………
(a) 109º 28’
(b) 107º 28’
(c) 104º
(d) 107º
Answer:
(d) 107º
Question 11.
Shape of ammonia is …………
(a) Planar
(b) Square planar
(c) Pyramidal
(d) Square pyramidal
Answer:
(c) Pyramidal
Question 12.
Nitric acid prepared in large scales using …………
(a) Ostwald’s process
(b) Haber’s process
(c) Contact process
(d) Deacon’s process
Answer:
(a) Ostwald’s process
Question 13.
Benzene undergoes nitration reaction to form nitrobenzene in this reaction takes place due to the formation of …………
(a) Hydronium ion
(b) Hydride ion
(c) Nitronium ion
(d) Nitrasonium ion
Answer:
(c) Nitronium ion
Question 14.
Oxidation state of N m FINO₃ is…………
(a) ±2
(b) +3
(c) +4
(d) +5
Answer:
(d) +5
Question 15.
Compound used in photography is …………
(a) AgNO₃
(b) AgBr
(c) AgCl
(d) AgI
Answer:
(a) AgNO₃
Question 16.
Sodium nitrate
(a) Photography
(b) Firearms
(c) Royal water Sosurgerv …………
(d) Cryosurgery
Answer:
(b) Firearms
Question 17.
Nitrogen sesquoxide colour is …………
(a) colourless
(b) Brown
(c) Blue
(d) Red
Answer:
(c) Blue
Question 18.
White phosphorous is also called as …………
(a) Red phosphorous
(b) Black phosphorous
(c) Scarlet phosphorous
(d) Yellow phosphorous
Answer:
(d) Yellow phosphorous
Question 19.
White (Yellow) phosphorous glows in the dark due to oxidation which is called …………
(a) phosphorescence
(b) phosphorus
(c) Fluorescence
(d) Liminoscence
Answer:
(a) phosphorescence
Question 20.
Yellow phosphorous reacts with alkali on boiling in an inert atmosphere liberates …………
(a) Phosphorous acid
(b) Phosphoric acid
(c) Phosphine
(d) Pyrophosphoric acid
Answer:
(c) Phosphine
Question 21.
Consider the following statements.
(i) phosphine is the most important hydride of phosphorous
(ii) phosphine is a poisonous gas with rotten egg smell.
(iii) phosphine is a powerful reducing agent
Which of the above statement(s) is / are correct?
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) only
Answer:
(c) (i) and (iii)
Question 22.
When phosphine is heated with air it bums to gives …………
(a) Orthophosphoric acid
(b) Metaphosphoric acid
(c) Pyrophosphoric acid
(d) Phosphoroustrioxide
Answer:
(b) Metaphosphoric acid
Question 23.
Hybridisation of P in phosphine is …………
(a) sp³d
(b) sp3d³
(c) sp³d³
(d) sp³
Answer:
(d) sp³
Question 24.
Compounds used in Holme’s signal are …………
(a) Phosphine + Acetylene
(b) H₃PO₃+H₃PO₃
(c) Calcium carbide + calcium phosphide
(d) Calcium carbonate + calcium phosphate
Answer:
(c) Calcium carbide + calcium phosphide
Question 25.
Chalgogens are also called as …………
(a) Ore forming elements
(b) Group-16 elements
(c) group 17 elements
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Question 26.
Element present in the volcanic ashes is …………
(a) Oxygen
(b) Sulphur
(c) Selenium
(d) Tellurium
Answer:
(b) Sulphur
Question 27.
The decomposition of potassium chlorate speed up in the presence of …………
(a) MnO₂
(h) Mn₃O₄
(c) MnSO₄
(d) KMnO₄
Answer:
(a) MnO₂
Question 28.
Pure ozone is …………
(a) yellow gas
(b) blue gas
(c) Pale blue gas
(d) bright blue gas
Answer:
(c) Pale blue gas
Question 29.
Shape of ozone …………
(a) V-shape
(b) Linear shape
(c) bent shape
(d) spherical shape
Answer:
(c) bent shape
Question 30.
The rate of decompositon of ozone drops sharply in …………
(a) acidic medium
(b) alkaline medium
(c) neutral medium
(d) Ether medium
Answer:
(b) alkaline medium
Question 31.
Which one of the following used as fuel in rockets?
(a) Liq O₂
(b) Liq CO₂
(c) Liq N₂
(d) Liq He – O₂
Answer:
(a) Liq O₂
Question 32.
Find out crystalline allotrophic form of sulphur?
(a) γ – sulphur
(b) λ – sulphur
(c) α – sulphur
(d) milk of sulphur
Answer:
(c) α – sulphur
Question 33.
Consider the following statements
(i) α – sulphur is the only thermodynamically stable allotrophic form.
(ii) At 140 º C the mono clinic sulphur melts to form mobile pale yellow liquid called γ – sulphur
(iii) Monoclinic sulphur is stable between 96ºC-119ºC and slowly changes into λ- sulphur
Which of the above statement(s) is / are not correct?
(a) (i) only
(b) (ii) only
(c) (iii) only
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Answer:
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Question 34.
Sulphur di oxide, how many times heavier than air?
(a) 2 times
(b) 2.5 times
(c) 2.2 times
(d) 2.3 times
Answer:
(c) 2.2 times
Question 35.
Which one of following has temporary bleaching action?
(a) Chlorine
(b) SO₃
(c) H₃SO₄
(d) SO₂
Answer:
(d) SO₂
Question 36.
Sulphuric acid can be manufactured by …………
(a) Ostwald’s process
(b) Lead chamber process
(c) Deacon’s process
(d) Haber’s process
Answer:
(b) Lead chamber process
Question 37.
Sulphuric acid is manufactured by contact process, catalyst used in contact process is …………
(a) V₂O₅
(b) TiCl₄
(c) Fe
(d) Mo
Answer:
(c) V₂O₅
Question 38.
Benzene reacts with sulphuric acid to gives …………
(a) sulphate
(b) sulphide
(c) sulphonic acid
(d) sulphite
Answer:
(c) sulphonic acid
Question 39.
Reagent used to detect sulphate ion is …………
(a) BaCl₂
(b) BaSO₃
(c) (CH,COO),Pb
(d) both (a) and (c)
Answer:
(d) both (a) and (c)
Question 40.
Deacon’s process is used to manufacture …………
(a) Cl₂
(b) F₂
(C) Br
(d) I₂
Answer:
(a) Cl₂
Question 41.
Catalyst used in Deacon’s process is …………
(a) CuCl₂
(b) Cu₂Cl₂
(c) CuBr
(d) Cu₂Br₂
Answer:
(b) Cu₂Cl₂
Question 42
C₁₀H1₁₆+ 8C₁₂ △→ A. Identify A?
(a) Methane
(b) Ethane
(c) Carbon
(d) Propane
Answer:
(c) Carbon
Question 43.
Passing chlorine gas through dry slaked lime to produce …………
(a) CaOCl
(b) CaOCl₂
(c) CaO
(d) CaCl₂
Answer:
(b) CaOCl₂
Question 44.
Which one of the following is used for purification of drinking water?
(a) SO₃
(b) SO₂
(c) Br₂ / H₂O
(d) Cl₂
Answer:
(d) Cl₂
Question 45.
Which one of the following is a weak acid?
(a) HF
(b) HCl
(c) HBr
(d) HI
Answer:
(a) HF
Question 46.
Reagent not stored in glass bottles?
(a) HCI
(b) HBr
(c) HF
(d) HI
Answer:
(c) HF
Question 47.
More reactive element is
(a) Fluorine
(b) Chlorine
(c) Bromine
(d) Iodine
Answer:
(a) Fluorine
Question 48.
The correct order of the acidity of hydrohalic acids?
(a) HF > HCI > HBr > HI
(b) HCI >HF >HBr >HI
(c) HBr > HCI >HF > HI
(d) HI > HBr > HCI > HF
Answer:
(d) HI > HBr > HCI > HF
Question 49.
Consider the following statements
(i) In interhalogen compounds, the central atom will be the smaller one.
(ii) It can be formed only between two halogen and not more than two halogens.
(iii) They are strong reducing agents.
Which of the above statement(s) is / are not correct?
(a) (i) only
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (iii) only
Answer:
(c) (i) and (iii)
Question 50.
Shape of ClF₃ is …………
(a) Linear
(b) T-shape
(c) Pyrimidal
(d) Square planar
Answer:
(b) T-shape
Question 51.
Which one of the following is more acidic?
(a) HOCl
(b) HCIO₂
(c) HClO₃
(d) HClO₄
Answer:
(d) HClO₄
Question 52.
When XeF₆ reacts with 2.5 M NaOH gives …………
(a) Na₄XeO₆
(b) Na2XeO₃
(c) XeO₂F₂
(d) XeO₃
Answer:
(a) Na₄XeO₆
Question 53.
Shape of XeF₆ is …………
(a) Octahedron
(b) Distorted octahedron
(c) Pyramidal
(d) Tetrahedron
Answer:
(b) Distorted octahedron
Question 54.
Which one of the following can penetrate through dense fog?
(a) He
(b) Ne
(c) Kr
(d) Rn
Answer:
(c) Kr
Question 55.
Find out radioactive element?
(a) He
(b) Rn
(c) Xe
(d) Ar
Answer:
(b) Rn
II. Fill in the blanks:
- The 11th most abundant element is ………….
- …………. is the principle gas of atmosphere.
- Nitrogen is chemically ………….
- …………. process for the synthesis of ammonia.
- …………. is used for the manufacture of calcium cyanamide
- …………. is a pungent smelling gas.
- Ammonia acts as a …………. agent.
- With excess of chlorine, ammonia reacts to give …………. an explosive substance.
- When excess ammonia is added to aqueous solution of copper sulphate …………. colour compound is formed.
- Pure nitric acid becomes …………. on standing.
- …………. is used in gunpower for firearms.
- The decomposition of ammonium nitrate gives ………….
- White phosphorous is colourless but becomes pale yellow due to formation of a …………. upon standing.
- The white phosphorous can be changed into …………. by heated it to 420°C in the absence of air and light.
- …………. reacts with alkali on boiling in an inert atmosphere liberating phosphine.
- …………. is used in the match boxes.
- Phosphine is …………. smelling gas.
- Phosphine has a …………. shape.
- …………. is used for producing smoke screen.
- When phosphorous trichloridie is hydrolysed with cold water it gives ………….
- Elements belonging group 16 are called ………….
- Under ordinary condition oxygen exists as a …………. gas.
- Allotrophic form of oxygen is …………. and ………….
- Pure ozone is …………. gas.
- …………. is used in welding purpose.
- Monoclinic sulphur is stable between 96° and 119°C and slowly changes into ………….
- …………. gas is found in volcanic eruptions.
- A large amount of …………. gas is released into atmosphere from plants using coal and oil and copper melting plants.
- Sulphurdioxide gas has …………. odour.
- Sulphurdioxide can be used for …………. and …………. in agriculture.
- In SO₃ S-atom undergoes …………. hybridisation.
- In SO₃ a double bond arises between S and O is due to …………. overlapping.
- High boiling point and viscosity of sulphuric acid is due to ………….
- …………. is used as a drying agent.
- The main source of fluorine is ………….
- The main source of chlorine is ………….
- Chlorine is a …………. gas.
- Chlorine is soluble in water and its solution is referred as ………….
- …………. is produced by passing chlorine gas through dry slaked lime.
- …………. is used in extraction of gold and platinum.
- …………. is used for extraction of glue from bone.
- At room temperature, hydrogen halides are gases but …………. can be readily liquefied.
- Liberation of iodine which gives a …………. colouration with starch.
- Each halogen combines with other halogens to form a series of compounds called ………….
- Structure of AX₇ type is ………….
- Oxidation state of Cl in HClO₄ is ………….
- Noble gases have the …………. ionisation energy.
- Xenon reacts with PtF₆ and gave an ………….
- Kr and fluorine gases are irradiated with SbF it forms ………….
- Shape of XeOF₄ is ………….
- Helium used for filling air ………….
- …………. is used in fluorescent bulbs.
- …………. is used in high speed electronic flash bulbs.
- Radon is a source of …………. rays.
- …………. is formed by the hydrolysis of urea.
- …………. element subtimes at 889 K.
- Yellow phosphorus has a characteristics …………. smell.
Answers:
- phosporous
- Nitrogen
- Inert
- Haber’s
- Nitrogen
- Ammonia
- Reducing
- Nitrogen trichloride
- Deep blue
- Yellow
- Nitric acid / NaNO
- Nitrous oxide
- Layer of red phosphorous
- Red phosphorous
- White phosphorous
- Red phosporous
- Rotten fish
- Pyramidal
- Phosphine
- phosporous acid
- Chalgogens
- diatomic
- dioxygen and ozone
- pale blue
- Oxyacetylene
- Rhombic sulphur
- Sulphurdioxide
- SO₂
- Suffocating
- disinfecting crops and plants
- sp²
- pπ – dπ
- Hydrogen bonding
- Sulphuric acid
- Fluorite
- Sodium chloride
- Green yellow
- Chlorine water
- Bleaching powder
- Chlorine
- Hydrochloric acid
- hydrogen fluroide
- blue-black
- Inter-halogen compounds
- pentagonal bipyramidal
- +7
- largest
- orange yellow solid [XePtF₆]
- KrF₂ 2SbF₆
- Square pyramidal
- Balloons
- Krypton
- Xenon
- Gamma
- Ammonia
- Arsenic
- Garlic
We understand your expectations These 12th chemistry guide solutions . book back Question and Additional Question and answer help for your Exam preparation.






Really Satisfied by ur answers tq��
ReplyDelete